In the ever-evolving landscape of anatomy and medical education, a groundbreaking technique has emerged that has captured the attention of artists, scientists, and the general public alike. We learned this the hard way… Plastination, pioneered by German anatomist Gunther von Hagens, has transformed the way we visualize and understand the human body, blending the realms of art and science in unprecedented ways.
Now, this might seem counterintuitive…
The Origins and Innovations of Plastination
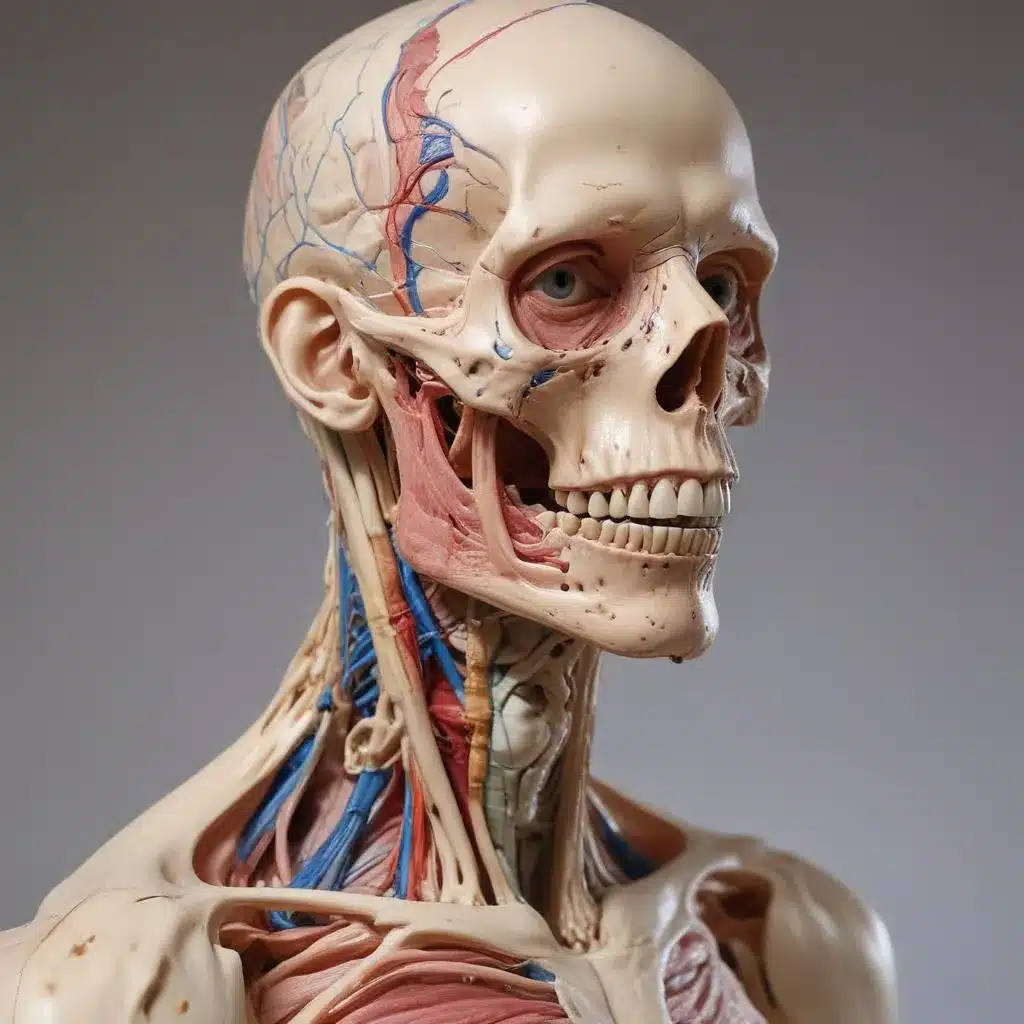
Plastination is a revolutionary preservation method that replaces the natural fluids in biological specimens with curable polymers, resulting in dry, odorless, and durable anatomical models. Developed in the late 1970s, this innovative process was initially met with skepticism, as it challenged the traditional approach to anatomy education and specimen conservation.
Von Hagens, the founder of the Institute for Plastination in Heidelberg, Germany, recognized the limitations of traditional dissection and embalming techniques. These methods often resulted in specimens that were difficult to handle, prone to deterioration, and lacked the level of detail necessary for comprehensive anatomical study. Driven by his passion for advancing medical education, von Hagens set out to revolutionize the field with his groundbreaking plastination technique.
The Plastination Process: Transforming the Human Form
The plastination process is a meticulous and intricate procedure that involves several key steps. First, the specimen is fixed, typically using a formaldehyde-based solution, to preserve the tissues and prevent decomposition. Next, the water and lipids within the specimen are removed through a process of dehydration and defatting, leaving behind the solid components.
The critical step in plastination is the replacement of the natural fluids with a curable polymer, such as silicone or epoxy resin. This is achieved by immersing the specimen in a polymer bath, where the liquid polymer gradually permeates the tissues, filling the spaces previously occupied by water and lipids. Once the polymer has fully penetrated the specimen, it is cured, typically through the application of heat or a chemical catalyst, resulting in a dry, durable, and lifelike anatomical model.
The final stage of the plastination process involves the careful positioning and posing of the specimen, often incorporating artistic elements to create visually striking and educational displays. These meticulously crafted anatomical artworks have found their way into medical schools, museums, and even art galleries, captivating audiences and challenging our perceptions of the human form.
The Artistic and Educational Impact of Plastination
The marriage of art and science in plastination has had a profound impact on both the medical and artistic communities. For medical students and healthcare professionals, plastinated specimens offer an unparalleled learning experience, allowing them to study the intricate details of human anatomy in a more accessible and interactive manner.
Traditionally, anatomy education has relied heavily on textbooks, diagrams, and cadaveric dissection, which can be challenging for students to fully grasp. Plastinated specimens, on the other hand, provide a tangible and visually striking representation of the human body, enabling students to explore the three-dimensional relationships between organs, muscles, and skeletal structures.
Beyond the realm of medical education, plastinated specimens have also captured the attention of the art world. Von Hagens’ groundbreaking “Body Worlds” exhibitions have toured the globe, showcasing the human form in a unique and thought-provoking manner. These exhibitions have not only sparked scientific curiosity but have also invited viewers to contemplate the nature of the human body, its fragility, and its capacity for transformation.
The Ethical Considerations of Plastination
While the artistic and educational benefits of plastination are undeniable, the technique has also raised important ethical considerations. The use of human remains for public display and artistic expression has been a subject of much debate, with concerns ranging from cultural and religious sensitivities to the potential exploitation of the deceased.
To address these concerns, plastination programs have implemented strict ethical guidelines and consent protocols, ensuring that donors voluntarily and explicitly provide permission for their bodies to be used in this manner. Additionally, many plastination exhibitions and educational programs emphasize the importance of respect, reverence, and the advancement of medical knowledge as the driving forces behind their work.
The Future of Plastination: Preserving the Past, Enhancing the Present
As the field of plastination continues to evolve, the potential for its applications extends far beyond the realm of anatomy education and artistic expression. The durability and longevity of plastinated specimens have made them invaluable tools for the conservation of rare and endangered species, allowing scientists and researchers to study and preserve the natural world in unprecedented detail.
Moreover, the versatility of plastination has opened up new avenues for the preservation of historical artifacts and cultural relics. Fragile and delicate materials, such as textiles, fossils, and ancient manuscripts, can be effectively stabilized and protected through the plastination process, ensuring their survival for future generations.
Conclusion: Embracing the Intersection of Art and Science
The art and science of plastination have revolutionized the way we perceive and interact with the human body, bridging the gap between the realms of medical education, scientific research, and artistic expression. As we continue to explore the boundless possibilities of this groundbreaking technique, we are reminded of the power of innovation, the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration, and the value of embracing the intersections between art and science.
Through the stunning and thought-provoking plastinated specimens, we are invited to marvel at the intricate complexity of the human form, to deepen our understanding of anatomy and physiology, and to consider the profound questions that arise at the intersection of art, science, and the human experience. As we navigate this captivating landscape, we are reminded of the enduring power of the “book of nature” and the transformative potential of the human mind.
Example: Modern Abstract Painting Series 2024